Admin
مدير المنتدى


عدد المساهمات : 18864
التقييم : 35108
تاريخ التسجيل : 01/07/2009
الدولة : مصر
العمل : مدير منتدى هندسة الإنتاج والتصميم الميكانيكى
 |  موضوع: كتاب The Basics of Hydraulic Systems موضوع: كتاب The Basics of Hydraulic Systems  الثلاثاء 24 مايو 2022, 2:35 am الثلاثاء 24 مايو 2022, 2:35 am | |
| 
أخواني في الله
أحضرت لكم كتاب
The Basics of Hydraulic Systems
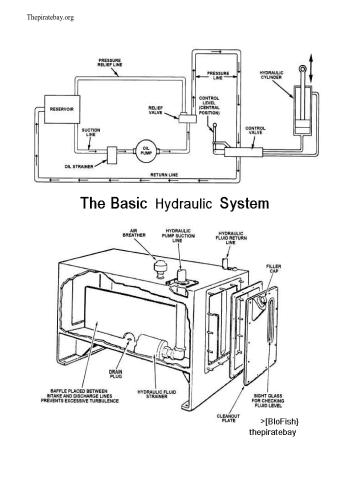
و المحتوى كما يلي :
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Section Page
Subcourse Overview . i
Administrative Instructions . iv
Grading and Certification Instructions iv
Lesson 1: Basic Hydraulics . 1
Practice Exercise . 19
Answer Key and Feedback . 22
Lesson 2: Hydraulic Plumbing 25
Practice Exercise . 69
Answer Key and Feedback . 71
Appendix A: Proof Testing of Hose Assemblies 72
Appendix B: Glossary 73
Examination . 78
Student Inquiry Sheet
Hydraulics
Table of Contents
Page
LIST OF FIGURES AND TABLES vii
Figures vii
Tables . xiii
PREFACE . xiv
CHAPTER 1. Hydraulic Basics . 1-1
1-1. Pressure and Force . 1-1
Pressure . 1-1
Force . 1-3
1-2. Pascal’s Law . 1-4
1-3. Flow . 1-6
Velocity . 1-6
Flow Rate . 1-6
1-4. Energy, Work, and Power . 1-6
Potential Energy . 1-6
Kinetic Energy . 1-6
Heat Energy and Friction . 1-6
Relationship Between Velocity and Pressure . 1-7
Work . 1-8
Power . 1-8
CHAPTER 2. Hydraulic Systems . 2-1
2-1. Basic Systems . 2-1
Hydraulic Jack . 2-1
Motor-Reversing System 2-1
Open-Center System . 2-2
Closed-Center System . 2-5
 OS-Software OS-Software
iFM 5-499
ii
Page
2-2. Color Coding 2-9
2-3. Reservoirs 2-9
Construction 2-9
Shape . 2-10
Size 2-10
Location . 2-10
Ventilation and Pressurization 2-11
Line Connections . 2-11
Maintenance . 2-11
2-4. Strainers and Filters 2-11
Strainers 2-12
Filters 2-12
2-5. Filtering Material and Elements . 2-14
2-6. Accumulators . 2-14
Spring-Loaded Accumulator 2-14
Bag-Type Accumulator . 2-15
Piston-Type Accumulator . 2-15
Maintenance . 2-15
2-7. Pressure Gauges and Volume Meters . 2-17
Pressure Gauges 2-17
Meters 2-17
2-8. Portable Hydraulic-Circuit Testers . 2-18
Testers 2-18
Improper Operation . 2-18
2-9. Circulatory Systems . 2-18
Tubing 2-19
Piping 2-19
Flexible Hosing . 2-19
Installation 2-21
2-10.Fittings and Connectors 2-21
Threaded Connectors 2-21
Flared Connectors . 2-23
Flexible-Hose Couplings 2-25
Reusable Fittings . 2-25
2-11.Leakage . 2-29
Internal . 2-29
External . 2-30
Prevention . 2-30
2-12.Seals 2-30
Static Seals 2-31
Dynamic Seals . 2-31
Packing . 2-33
Seal Materials 2-34FM 5-499
iii
Page
CHAPTER 3. Pumps . 3-1
3-1. Pump Classifications . 3-1
Nonpositive-Displacement Pumps 3-1
Positive-Displacement Pumps 3-1
Characteristics 3-2
3-2. Performance 3-2
3-3. Displacement . 3-2
Fixed-Displacement Pump . 3-3
Variable-Displacement Pump 3-3
3-4. Slippage 3-3
3-5. Designs 3-3
Centrifugal Pump 3-3
Rotary Pump 3-4
Reciprocating Pump 3-4
3-6. Gear Pumps 3-4
External . 3-4
Internal 3-5
Lobe Pump . 3-6
3-7. Vane Pumps 3-6
Characteristics 3-6
Unbalanced Vane Pumps 3-6
Balanced Vane Pumps 3-7
Double Pumps 3-7
Two-Stage Pumps 3-9
3-8. Piston Pumps 3-10
Radial 3-10
Axial Piston Pumps . 3-11
3-9. Pump Operation 3-14
Overloading . 3-14
Excess Speed 3-14
Cavitation . 3-14
Operating Problems . 3-15
CHAPTER 4. Hydraulic Actuators . 4-1
4-1. Cylinders . 4-1
Single-Acting Cylinder 4-1
Double-Acting Cylinder . 4-1
Differential Cylinder . 4-1
Nondifferential Cylinder 4-2
Ram-Type Cylinder 4-2
Piston-Type Cylinder . 4-3
Cushioned Cylinder 4-4
Lockout Cylinders . 4-4
4.2 Construction and Application 4-4FM 5-499
iv
Page
4-3. Maintenance 4-5
External Leakage 4-5
Internal Leakage 4-5
Creeping Cylinder 4-5
Sluggish Operation . 4-5
Loose Mounting . 4-5
Misalignment . 4-5
Lack of Lubrication . 4-7
Abrasives on a Piston Rod . 4-7
Burrs on a Piston Rod 4-7
Air Vents . 4-7
4-4. Hydraulic Motors 4-7
Gear-Type Motors 4-8
Vane-Type Motors 4-8
Piston-Type Motors 4-10
CHAPTER 5. Valves . 5-1
5-1. Pressure-Control Valves . 5-1
Relief Valves 5-2
Pressure-Reducing Valves . 5-3
Sequence Valves . 5-5
Counterbalance Valves 5-7
Pressure Switches 5-8
5-2. Directional-Control Valves . 5-8
Poppet Valve 5-9
Sliding-Spool Valve 5-10
Check Valves . 5-10
Two-Way Valve . 5-14
Four-Way Valves . 5-14
5-3. Flow-Control Valves . 5-19
Gate Valve . 5-19
Globe Valve 5-21
Needle Valve . 5-22
Restrictor 5-22
Orifice Check Valve . 5-23
Flow Equalizer . 5-23
5-4. Valve Installation . 5-25
Meter-In Circuit 5-25
Meter-Out Circuit . 5-25
Bleed-Off Circuit 5-26
Compensated Flow 5-26
5-5. Valve Failures and Remedies 5-26
Servicing Valves 5-27
Disassembling Valves 5-27
Repairing Valves 5-28FM 5-499
v
Page
5-6. Valve Assembly . 5-29
5-7. Troubleshooting Valves 5-30
Pressure-Control Valves . 5-30
Directional-Control Valves . 5-32
Volume-Control Valves 5-33
CHAPTER 6. Circuit Diagrams and Troubleshooting . 6-1
6-1. Hydraulic-Circuit Diagrams . 6-1
6-2. United States of American Standards Institute (USASI) Graphical . 6-1
Symbols
Reservoir . 6-4
Lines 6-4
Pump 6-4
Motor 6-5
Cylinder . 6-5
Pressure-Control Valves 6-5
Flow-Control Valves 6-7
Directional-Control Valves 6-7
Accessories . 6-9
6-3. Typical Mobile Circuits 6-11
Hydraulic-Lift Circuit . 6-11
Power-Steering Circuits 6-12
Road-Patrol-Truck Circuits . 6-12
6-4. Troubleshooting 6-13
Causes of Improper Operations 6-13
Testing a Hydraulic Circuit . 6-13
Comparing Test Results with Specifications . 6-13
Slippage 6-15
Flow and Pressure 6-15
Other Conditions . 6-15
Specific Troubles, Causes, and Solutions 6-16
CHAPTER 7. Electrical Devices: Troubleshooting and Safety . 7-1
7-1. Hydraulics and Electricity . 7-1
7-2. Troubleshooting Electrical Devices 7-1
Procedure 7-5
Testing Devices . 7-6
7-3. Ground 7-8
Earth Ground . 7-8
Chassis or Common Ground . 7-9
Zero Reference Point . 7-9
Isolation Between Earth and Chassis Ground 7-10
7-4. Safety 7-10
Information 7-10
Practices 7-11FM 5-499
vi
Page
APPENDIX A. Metric Conversion Chart . Appendix-1
GLOSSARY Glossary-1
REFERENCES . References-1
INDEX . Index-1
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Section Page
Subcourse Overview . i
Terminal Learning Objective . ii
Administrative Instructions . iv
Grading and Certification Instructions iv
Lesson 1: Hydraulic Reservoirs, Filters, Pumps,
Accumulators, and Motors 1
Practice Exercise . 19
Answer Key and Feedback . 22
Lesson 2: Basic Construction and Operation of Hydraulic
Actuating Devices, Flow Control, and Directional
Devices . 25
Practice Exercise . 43
Answer Key and Feedback . 46
Lesson 3: Hydraulic Pressure-Limiting, Controlling, and
Sensing Devices . 49
Practice Exercise . 55
Answer Key and Feedback . 58
Examination 61
Appendix: Glossary . 69
Student Inquiry Sheets
Engineering and Design
DESIGN OF HYDRAULIC STEEL
STRUCTURES
Table of Contents
Subject Paragraph Page Subject Paragraph Page
Chapter 1 Commentary on Paragraph 3-4,
Introduction Reliability Factors for HSS . 3-8 3-2
Purpose 1-1 1-1 Commentary on Paragraph 3-6, Fatigue
Applicability 1-2 1-1 and Fracture Control 3-9 3-3
References 1-3 1-1
Background . 1-4 1-1 Chapter 4
Commentary on Paragraph 1-4, Allowable Stress Design
Background 1-5 1-1 General . 4-1 4-1
Design Basis . 4-2 4-1
Chapter 2 Load and Stress Requirements . 4-3 4-1
General Considerations HSS Types: Modifications for
Limit States 2-1 2-1 Allowable Stresses . 4-4 4-1
Corrosion 2-2 2-1 Serviceability Requirements 4-5 4-1
Dynamic Loading 2-3 2-1 Fatigue and Fracture Control . 4-6 4-1
Inspection and Maintenance 2-4 2-1 Commentary on Paragraph 4-3, Load and
Deviations from Prescribed Stress Requirements . 4-7 4-2
Design 2-5 2-1 Commentary on Paragraph 4-4, HSS Types:
Commentary on Paragraph 2-2, Modifications for Allowable
Corrosion 2-6 2-1 Stresses 4-8 4-2
Commentary on Paragraph 2-3, Dynamic
Loading 2-7 2-2 Chapter 5
Connections and Details
Chapter 3 General . 5-1 5-1
Load and Resistance Factor Design Design Considerations 5-2 5-1
General . 3-1 3-1 Bolted Connections 5-3 5-1
Design Basis . 3-2 3-1 Welded Connections . 5-4 5-1
Strength Requirements 3-3 3-1 Commentary on Paragraph 5-1,
Reliability Factors for HSS 3-4 3-1 General 5-5 5-1
Serviceability Requirements 3-5 3-1 Commentary on Paragraph 5-2,
Fatigue and Fracture Control . 3-6 3-2 Design Considerations 5-6 5-2
Commentary on Paragraph 3-2, Design
Basis 3-7 3-2
iEM 1110-2-2105
Change 1
31 May 94
Subject Paragraph Page
Commentary on Paragraph 5-3, Bolted
Connections 5-7 5-2
Commentary on Paragraph 5-4, Welded
Connections 5-8 5-2
Appendix A
References
Appendix B
Load and Resistance Factor Design
Criteria for Miter Gates
Appendix C
Tainter Gates
Appendix D
Tainter Valves
Appendix E
Bulkheads and Stoplogs
Appendix F
Vertical Lift Gates (Lock and Crest)
Appendix G
Hydroelectric and Pumping Plants
* Appendix H
Flood Closure Structures
Appendix I
Miscellaneous Hydraulic Steel Structures
Figure Page
B-1. Point load impact for miter
gate girders . B-3
B-2. Assumptions for intercostal
end connections B-5
B-3. Nomenclature and assumed load
area for intercostal design . B-6
B-4. Vertical cross section for
example miter gate B-8
B-5. Example miter gate loading B-9
Figure Page
B-6. Nomenclature for skin plate
design . B-11
B-7. Sample intercostal section . B-12
B-8. Girder hydrostatic loading and
reactions . B-14
B-9. Sample girder cross section B-14
B-10. Example miter leaf torsion loads . B-19
Engineering and Design
LUBRICANTS AND HYDRAULIC FLUIDS
Table of Contents
Subject Paragraph Page
Chapter 1
Introduction
Purpose . 1-1 1-1
Applicability 1-2 1-1
References . 1-3 1-1
Distribution Statement . 1-4 1-1
Scope 1-5 1-2
Chapter 2
Lubrication Principles
Friction 2-1 2-1
Wear . 2-2 2-4
Lubrication and Lubricants 2-3 2-6
Hydrodynamic or Fluid Film Lubrication 2-4 2-6
Boundary Lubrication 2-5 2-8
Extreme Pressure (EP) Lubrication 2-6 2-9
Elastohydrodynamic (EHD) Lubrication . 2-7 2-9
Chapter 3
Lubricating Oils
Oil Refining . 3-1 3-1
Types of Oil 3-2 3-2
Characteristics of Lubricating Oils . 3-3 3-4
Oil Classifications and Grading Systems 3-4 3-7
Chapter 4
Hydraulic Fluids
Purpose of Hydraulic Fluids . 4-1 4-1
Physical Characteristics . 4-2 4-1
Quality Requirements . 4-3 4-2
Use of Additives 4-4 4-4
Types of Hydraulic Fluids . 4-5 4-4
Cleanliness Requirements . 4-6 4-6
iEM 1110-2-1424
28 Feb 99
ii
Subject Paragraph Page
Chapter 5
Grease
Description . 5-1 5-1
Function . 5-2 5-1
Grease Characteristics . 5-3 5-2
Fluid Lubricants . 5-4 5-5
Soap Thickeners . 5-5 5-5
Complex Soap . 5-6 5-6
Additives . 5-7 5-6
Types of Greases . 5-8 5-6
Compatibility 5-9 5-8
Grease Application Guide . 5-10 5-8
Chapter 6
Nonfluid Lubrication
Solid Lubrication . 6-1 6-1
Self-Lubricating Bearings 6-2 6-6
Self-Lubricating Bearings for Olmsted Wicket Gates Prototype Tests 6-3 6-7
Chapter 7
Lubricant Additives
General 7-1 7-1
Surface Additives . 7-2 7-1
Performance-Enhancing Additives 7-3 7-3
Lubricant Protective Additives . 7-4 7-3
Precautions . 7-5 7-4
Chapter 8
Environmentally Acceptable Lubricants
General 8-1 8-1
Definition of Environmentally Acceptable (EA) Lubricants 8-2 8-1
Biodegradation . 8-3 8-2
Toxicity 8-4 8-3
EA Base Fluids and Additives . 8-5 8-3
Properties of Available EA Products 8-6 8-6
Environmentally Acceptable Guidelines 8-7 8-8
Changing from Conventional to EA Lubricants . 8-8 8-8
Survey of Corps Users . 8-9 8-9
USACE Contacts 8-10 8-10
Chapter 9
Gears
General 9-1 9-1
Gear Types . 9-2 9-1
Gear Wear and Failure . 9-3 9-2
Gear Lubrication . 9-4 9-6EM 1110-2-1424
28 Feb 99
iii
Subject Paragraph Page
Chapter 10
Bearings
General . 10-1 10-1
Plain Bearings 10-2 10-1
Rolling-Contact Bearings 10-3 10-6
Calculation of Bearing Lubrication Interval 10-4 10-12
Chapter 11
Lubrication Applications
Introduction 11-1 11-1
Turbines, Generators, Governors, and Transformers 11-2 11-1
Main Pumps and Motors 11-3 11-5
Gears, Gear Drives, and Speed Reducers 11-4 11-6
Couplings . 11-5 11-8
Hoists and Cranes . 11-6 11-9
Wire Rope Lubrication . 11-7 11-10
Chain Lubrication . 11-8 11-14
Trashrake Systems and Traveling Water Screens 11-9 11-17
Gates and Valves . 11-10 11-17
Navigation Lock Gates, Culvert Valves, and Dam Gates . 11-11 11-24
Information Sources for Lubricants . 11-12 11-26
Chapter 12
Operation and Maintenance Considerations
Introduction 12-1 12-1
Maintenance Schedules . 12-2 12-1
Relative Cost of Lubricants 12-3 12-1
Lubricating Oil Degradation 12-4 12-4
Hydraulic Oil Degradation . 12-5 12-5
Transformer and Circuit Breaker Insulating Oil Degradation . 12-6 12-6
Essential Properties of Oil . 12-7 12-7
Other Properties of Used Oils . 12-8 12-8
Oil Monitoring Program . 12-9 12-9
Oil Purification and Filtration . 12-10 12-14
Oil Operating Temperature . 12-11 12-21
Lubricant Storage and Handling 12-12 12-22
Safety and Health Hazards 12-13 12-28
Environmental Regulations 12-14 12-29
Chapter 13
Lubricant Specifications and Selection
Introduction 13-1 13-1
Lubricant Classification . 13-2 13-1
Principles of Selection 13-3 13-4
Specification Types 13-4 13-9
Lubricant Consolidation . 13-5 13-10EM 1110-2-1424
31 Jul 06
Change 1
iv
Appendix A
References
Appendix B
Survey of Locks and Dams for Lubricants
Appendix C
Specification for Turbine Oil
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. GENERAL
2. REFERENCES
3. SUBMITTALS
4. TURBINE OIL CHARACTERISTICS AND REQUIREMENTS
5. COMPATIBILITY
6. PRE-DELIVERY TESTING
7. DELIVERY
8. INSPECTION AND ACCEPTANCE.
1. GENERAL
This specification covers zinc and chlorine-free rust and oxidation inhibited (R&O) mineral oils for
use in hydraulic turbine and generator bearings, Kaplan turbine hubs, hydraulic-turbine governors,
and other applications, where high-grade turbine oil having anti-corrosion, anti-oxidation, and
anti-foaming properties is required.
2. REFERENCES
The publications listed below form a part of this specification to the extent referenced. The
publications are referred to in the text by basic designation only.
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS (ASTM)
ASTM D 92 (2002b) Flash and Fire Points by Cleveland Open
Cup
ASTM D 97 (2004) Pour Point of Petroleum Oils
ASTM D 130 (2004) Corrosiveness to Copper from Petroleum
Products by Copper Strip Test
ASTM D 445 (2004e1) Kinematic Viscosity of Transparent and
Opaque Liquids (and the Calibration of Dynamic
Viscosity)
ASTM D 664 (2004e1) Acid Number of Petroleum Products by
Potentiometric Titration
ASTM D 665 (2003) Rust-Preventing Characteristics of Inhibited
Mineral Oil in the Presence of Water
C-3EM 1110-2-1424
26 Oct 07
Change 2
ASTM D 892 (2003) Foaming Characteristics of Lubricating Oils
ASTM D 943 (2004a) Oxidation Characteristics of Inhibited
Mineral Oils
ASTM D 1401 (2002) Water Separability of Petroleum Oils and
Synthetic Fluids
ASTM D 2270 (2004) Calculating Viscosity Index from Kinematic
Viscosity at 40 and 100 Degrees C
ASTM D 2272 (2002) Oxidation Stability of Steam Turbine Oils by
Rotating Pressure Vessel Oxidation Test
ASTM D 3427 (2003) Air Release Properties of Petroleum Oils
ASTM D 4057 (2000) Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
Petroleum ProductsASTM D 4177 (2000)
Automatic Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum
Products)
ASTM D 6304 (2004ae1) Water in Petroleum Products, Lubricating
Oils, and Additives by Coulometric Karl Fisher
Titration
ASTM D 7155 (2006) Standard Practice for Evaluating
Compatibility of Mixtures of Turbine Lubricating
Oils
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION (ISO)
ISO 4406 (1999) Coding the Level of Contamination by Solid
Particles
ISO 11171 (1999) Calibration Of Automatic Particle Counters
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Section Page
Subcourse Overview i
Administrative Instructions .iii
Grading and Certification Instructions iv
Lesson 1: Hydraulic Pumps .11
Part A: PositiveDisplacement Pumps .12
Part B: Gear Pump .15
Part C: Vane Pump .111
Part D: Piston Pump .112
Practice Exercise .119
Answer Key and Feedback .122
Lesson 2: Hydraulic Valves 21
Part A: PressureControl Valves .22
Part B: DirectionalControl Valves .25
Part C ControlValve Repair .28
Practice Exercise .215
Answer Key and Feedback .218
Examination E1
Appendix A: List of Common Acronyms .A1
Appendix B: Recommended Reading List B1
Appendix C: Metric Conversion Chart .C1
iii EN 5260Appendix D: Publication Extracts .D1
Student Inquiry Sheets
Table of Contents
Subject Paragraph Page
CHAPTER 1. INTRODUCTION
Purpose 1-1 1-1
Applicability 1-2 1-1
References 1-3 1-1
Background 1-4 1-2
General Requirements 1-5 1-3
Scope 1-6 1-3
Computer Programs 1-7 1-3
Rescission 1-8 1-3
CHAPTER 2. DETAILS OF REINFORCEMENT
General 2-1 2-1
Quality 2-2 2-1
Anchorage, Bar Development, and Splices 2-3 2-1
Hooks and Bends 2-4 2-1
Bar Spacing 2-5 2-1
Concrete Protection for Reinforcement 2-6 2-2
Splicing 2-7 2-2
Temperature and Shrinkage Reinforcement 2-8 2-3
CHAPTER 3. STRENGTH AND SERVICEABILITY REQUIREMENTS
General 3-1 3-1
Stability Analysis 3-2 3-1
Required Strength 3-3 3-2
Design Strength of Reinforcement 3-4 3-6
Maximum Tension Reinforcement 3-5 3-6
Control of Deflections and Cracking 3-6 3-6
Minimum Thickness of Walls 3-7 3-
STRENGTH AND SERVICEABILITY COMMENTARY
General
Stability Analysis
Required Strength
CHAPTER 4. FLEXURAL AND AXIAL LOADS
Design Assumptions and General
Requirements
Flexural and Compressive
Capacity - Tension
Reinforcement Only
Flexural and Compressive
Capacity - Tension and Compression
Reinforcement
Flexural and Tensile Capacity
Biaxial Bending and Axial Load
CHAPTER 5. SHEAR
Shear Strength
Shear Strength for Special Straight
Members
Shear Strength for Curved Members
Empirical Approach
APPENDICES
Appendix A Notation A-1
Appendix B Derivation of Equations for
Flexural and Axial Loads
B-l
Appendix C Investigation Examples C-l
Appendix D Design Examples D-l
Appendix E Interaction Diagram E-l
Appendix F Axial Load with Biaxial Bending -
Example
كلمة سر فك الضغط : books-world.net
The Unzip Password : books-world.net
أتمنى أن تستفيدوا من محتوى الموضوع وأن ينال إعجابكم
رابط من موقع عالم الكتب لتنزيل كتاب The Basics of Hydraulic Systems
رابط مباشر لتنزيل كتاب The Basics of Hydraulic Systems 
|
|
Dr.Mansour
مهندس تحت الاختبار


عدد المساهمات : 3
التقييم : 3
تاريخ التسجيل : 27/12/2019
العمر : 73
الدولة : Egypt
العمل : G.Manager
الجامعة : MTC
 |  موضوع: رد: كتاب The Basics of Hydraulic Systems موضوع: رد: كتاب The Basics of Hydraulic Systems  الثلاثاء 31 مايو 2022, 5:40 pm الثلاثاء 31 مايو 2022, 5:40 pm | |
| 
Thanks Dr. Eng. Mansour Soliman |
|







