Admin
مدير المنتدى


عدد المساهمات : 18726
التقييم : 34712
تاريخ التسجيل : 01/07/2009
الدولة : مصر
العمل : مدير منتدى هندسة الإنتاج والتصميم الميكانيكى
 |  موضوع: كتاب Refrigeration and Air Conditioning موضوع: كتاب Refrigeration and Air Conditioning  الخميس 10 نوفمبر 2022, 1:32 am الخميس 10 نوفمبر 2022, 1:32 am | |
| 
أخواني في الله
أحضرت لكم كتاب
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning
Ramesh Chandra Arora
Formerly Professor
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur
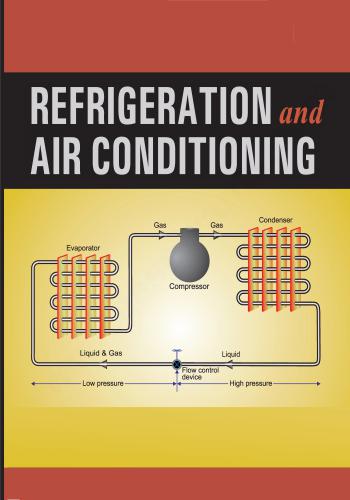
و المحتوى كما يلي :
Contents
Preface xiii
Acknowledgements xv
1 History of Refrigeration 1–18
1.1 Introduction 1
1.2 Natural Cooling Processes 2
1.3 Mechanical Cooling Processes 3
References 17
Review Questions 17
2 Thermal Principles—A Review of Fundamentals 19–96
2.1 Introduction 20
2.2 Thermodynamic Properties 20
2.3 Closed and Open Systems 21
2.4 Units 22
2.5 The Four Laws of Thermodynamics 28
2.6 Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics 28
2.7 First Law of Thermodynamics 29
2.8 First Law of Thermodynamics for Open Systems 31
2.9 Second Law of Thermodynamics 32
2.10 Fundamental Relations of Thermodynamics 36
2.11 Third Law of Thermodynamics 38
2.12 Perfect Gas 38
2.13 Mixture of Ideal Gases 39
2.14 Real Gas and Vapours 40
2.15 Dry Air 42
2.16 Properties of Pure Substance 43
vi Contents
2.17 Correlations for Properties of Refrigerants 49
2.18 Heat Transfer 50
2.19 Conduction 50
2.20 Fick’s Law of Diffusion 53
2.21 Thermal Radiation 54
2.22 Convection 59
2.23 Condensation Heat Transfer 66
2.24 Boiling Heat Transfer 67
2.25 Reynolds Analogy 69
2.26 Analogy between Heat, Mass and Momentum Transfer 69
2.27 Heat Transfer through Composite Walls and Cylinder 70
2.28 Heat Exchangers 75
2.29 Fluid Flow 77
2.30 Cooling Processes 85
References 95
Review Questions 95
3 Mechanical Vapour Compression Cycles 97–170
3.1 Introduction 98
3.2 Vapour Compression Cycle 98
3.3 Refrigeration Capacity 99
3.4 Coefficient of Performance 99
3.5 Reversed Carnot Cycle or Carnot Refrigeration Cycle 100
3.6 External Regime and Internal Regime 106
3.7 Gas as Refrigerant 108
3.8 Pure Substance as Refrigerant 116
3.9 Standard Vapour Compression Cycle or Vapour compression Cycle
or Single Stage Saturation (SSS) Cycle 121
3.10 Representation of Work as Areas on the T–s Diagram 125
3.11 Comparison of Standard Refrigeration Cycle with Reversed Carnot Cycle 126
3.12 Refrigerant Tables—Thermodynamic Properties 130
3.13 Subcooling and Superheating 132
3.14 Performance of Single Stage Saturation Cycle 137
3.15 Effect of Refrigerant Properties 141
3.16 Suction State for Optimum COP, Ewing’s Construction 143
3.17 Actual Cycle Diagram 148
Review Questions 169
4 Compressors 171–241
4.1 Introduction 172
4.2 Thermodynamics of Compression 172
4.3 Reciprocating Compressors 177
4.4 Hermetic Compressors 197
4.5 Rotary Compressors 205
4.6 Centrifugal Compressors 214
4.7 Comparison with Reciprocating Compressor 235
4.8 Capacity Control 238
Contents vii
4.9 Selection of Compressors 239
References 240
Review Questions 241
5 Performance of Single Stage Saturation Cycle
with Reciprocating Compressor 242–268
5.1 Introduction 243
5.2 Volumetric Efficiency and Mass Flow Rate 245
5.3 Work Requirement and HP/TR 246
5.4 Specific Refrigeration Effect and Refrigeration Capacity 247
5.5 Swept Flow Rate per TR 248
5.6 Adiabatic Discharge Temperature 249
5.7 Coefficient of Performance 250
5.8 Methods of Improving COP 250
5.9 Choice of Intermediate Pressure 254
5.10 Optimum Intermediate Pressure for Ideal Gas Compressor with
Ideal Intercooling 255
5.11 Optimum Intermediate Pressure if Intercooling is Done Up to
Temperature Tw 258
5.12 Optimum Intermediate Pressures for Three-Stage Compression 259
Reference 267
Review Questions 267
6 Multistage Refrigeration Systems 269–349
6.1 Introduction 270
6.2 Two-stage NH3 Cycle 270
6.3 Recommended Temperature Ranges for Multistage Systems 291
6.4 Multi-evaporator Systems 303
6.5 Two-stage Reversed Carnot Cycle 316
6.6 Limitations of Multistage Systems 318
6.7 Cascade Refrigeration System 320
6.8 Dry Ice Manufacture 337
6.9 Auto-cascade System 347
References 348
Review Questions 348
7 Absorption Refrigeration Systems 350–409
7.1 Introduction 351
7.2 Absorption Cycle of Operation 351
7.3 Maximum COP 353
7.4 Properties of Solutions 354
7.5 Aqua–Ammonia Solution 360
7.6 Simple Absorption System 369
7.7 h–x Diagram for Simple Absorption System 373
7.8 Drawbacks of Presence of Water Vapour in Evaporator and Condenser 379
7.9 Ammonia Enrichment Process 380
7.10 Water–Lithum Bromide Absorption Refrigeration System 393
7.11 The Platen–Munters System 404
viii Contents
7.12 Properties of Refrigerant Pairs for Absorption Systems 407
7.13 Comparison of Absorption System with Mechanical Vapour
Compression Refrigeration System 408
References 408
Review Questions 409
8 Refrigerants 410–471
8.1 Introduction 410
8.2 Designation of Refrigerants 411
8.3 Some Commonly Used Refrigerants 414
8.4 Desirable Properties of Refrigerants 415
8.5 Reaction with Lubricating Oil 423
8.6 Reaction with Moisture 425
8.7 Thermodynamic Properties 426
8.8 Alternative Refrigerants 432
8.9 Mixtures 436
8.10 Alternatives to Various Popular Refrigerants 456
8.11 Natural Refrigerants 462
8.12 Secondary Refrigerants 465
References 468
Review Questions 470
9 Expansion Valves 472–504
9.1 Introduction 473
9.2 Capillary Tube 473
9.3 Automatic Expansion Valve 486
9.4 Thermostatic Expansion Valve 492
9.5 Float Type Expansion Valve 499
9.6 Electronic Type Expansion Valve 501
9.7 Some Practical Problems in Operation of Expansion Valves 502
References 503
Review Questions 503
10 Condensers 505–548
10.1 Introduction 505
10.2 Heat Rejection Ratio 506
10.3 Types of Condensers 506
10.4 Comparison of Water-cooled and Air-cooled Condensers 507
10.5 Comparison of Water-cooled and Evaporative Condensers 508
10.6 Air-cooled Condenser 508
10.7 Mean Temperature Difference for Crossflow Heat Exchanger 510
10.8 Fin Efficiency 514
10.9 Heat Transfer Areas 520
10.10 Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient 522
10.11 Heat Transfer Coefficients 523
10.12 Water Cooled Condensers 530
References 547
Review Questions 548
Contents ix
11 Evaporators 549–570
11.1 Introduction 549
11.2 Classification of Evaporators 549
11.3 Natural Convection Coils 550
11.4 Flooded Evaporator 551
11.5 Shell-and-Tube Liquid Chillers 552
11.6 Direct Expansion Coil 556
11.7 Plate Surface Evaporators 556
11.8 Finned Evaporators 558
11.9 Boiling Heat Transfer Coefficients 567
Reference 570
Review Questions 570
12 Complete Vapour Compression System 571–582
12.1 Introduction 571
12.2 Reciprocating Compressor Performance Characteristics 572
12.3 Condenser Performance Characteristics 573
12.4 Evaporator Performance Characteristics 576
12.5 Expansion Valve Characteristics 577
12.6 Condensing Unit characteristics 577
12.7 Performance of Complete System—Condensing Unit and Evaporator 579
12.8 Effect of Expansion Valve 581
12.9 Conclusion 581
Reference 582
Review Questions 582
13 Gas Cycle Refrigeration 583–658
13.1 Introduction 583
13.2 Ideal Gas Behaviour 584
13.3 Temperature Drop Due to Work Output 584
13.4 Temperature Drop in Steady Flow Due to Change in Kinetic Energy 585
13.5 Temperature Drop in Closed System Due to Change in Kinetic Energy 586
13.6 Reversed Carnot and Joule Cycles for Gas Refrigeration 586
13.7 Aircraft Refrigeration Cycles 608
13.8 Vortex Tube Refrigeration 633
13.9 Pulse Tube 637
13.10 Stirling Cycle 641
13.11 Air Liquefaction Cycles 648
Review Questions 656
14 Water—Steam Ejector—Refrigeration System and
Thermoelectric Refrigeration System 659–688
14.1 Introduction 659
14.2 Principle of Operation 660
14.3 Centrifugal Compressor-Based System 661
14.4 Steam-Jet Ejector System 664
x Contents
14.5 Thermoelectric Refrigeration or Electronic Refrigeration 674
Reference 687
Review Questions 687
15 Air Conditioning 689–695
15.1 Historical Review 689
15.2 HVAC Systems 691
15.3 Classifications 692
References 695
Review Questions 695
16 Thermodynamic Properties of Moist Air 696–730
16.1 Mixtures of Gases 697
16.2 Amagat–Leduc’s Law 697
16.3 Gibbs–Dalton’s Law 699
16.4 Properties of Air–Water Vapour Mixture 701
16.5 Specific Humidity or Humidity Ratio 707
16.6 Humidity Ratio at Saturation 707
16.7 Degree of Saturation 709
16.8 Relative Humidity 709
16.9 Dew Point 710
16.10 Enthalpy of Moist Air 711
16.11 Humid Specific Heat 711
16.12 Thermodynamic Wet-Bulb Temperature 712
16.13 Goff and Gratch Tables 715
16.14 Psychrometric Charts 724
16.15 Typical Air Conditioning Processes 730
Review Questions 730
17 Elementary Psychrometric Processes 731–759
17.1 Introduction 731
17.2 Sensible Heating or Cooling of Moist Air 732
17.3 Humidification 734
17.4 Pure Humidification 736
17.5 Combined Heating and Humidification or Cooling and Dehumidification 737
17.6 Adiabatic Mixing of Two Streams of Moist Air 740
17.7 Adiabatic Mixing of Two Streams with Condensation 742
17.8 Air Washer 752
17.9 Adiabatic Dehumidification 756
17.10 Dehumidification by Hygroscopic Spray 757
17.11 Sprayed Coils 758
Review Questions 758
18 Wetted Surface Heat Transfer—Psychrometer, Straight Line Law
and Psychrometry of Air Conditioning Processes 760–818
18.1 Introduction 761
18.2 Heat and Mass Transfer Relations 761
18.3 Theory of Psychrometer 765
Contents xi
18.4 Humidity Standards 781
18.5 Other Methods of Measuring Humidity 782
18.6 Cooling and Dehumidification through Cooling Coil 783
18.7 Air Conditioning System 790
References 817
Review Questions 817
19 Comfort—Physiological Principles, IAQ and
Design Conditions 819–871
19.1 Introduction 820
19.2 Mechanical Efficiency of Humans 820
19.3 Metabolic Heat 820
19.4 Energy Balance and Models 823
19.5 Energy Exchange with Environment 824
19.6 Thermoregulatory Mechanisms 832
19.7 Heat Transfer Coefficients 834
19.8 Environmental Parameters 836
19.9 Application of Physiological Principles to Comfort
Air Conditioning Problems 837
19.10 Prediction of Thermal Comfort and Thermal Sensation 839
19.11 Standard Effective Temperature and Modified Comfort Chart 843
19.12 Effect of Other Variables on Comfort 846
19.13 Indoor Air Quality 847
19.14 Inside Design Conditions 861
19.15 Outdoor Design Conditions 864
References 870
Review Questions 871
20 Solar Radiation 872–902
20.1 Introduction 872
20.2 Sun 873
20.3 Earth 873
20.4 Basic Solar Angles 875
20.5 Time 876
20.6 Derived Solar Angles 878
20.7 Angle of Incidence 882
20.8 Solar Radiation Intensity 888
20.9 The Radiation Intensity on Earth’s Surface 890
20.10 Shading of Surfaces from Direct Radiation 897
References 902
Review Questions 902
21 Load Calculations 903–992
21.1 Introduction 904
21.2 Steady-State Heat Transfer through a Homogeneous Wall 904
21.3 Non-homogeneous Wall 906
21.4 Solar Radiation Properties of Surfaces 913
21.5 Radiation Properties of Diathermanous Materials 915
xii Contents
21.6 Heat Balance for the Glass 922
21.7 Periodic Heat Transfer through Walls and Roofs 936
21.8 Z-Transform Methods 954
21.9 Infiltration 956
21.10 Water Vapour Transfer through Building 970
21.11 Load Calculations—General Considerations 971
21.12 Internal Heat Gains 972
21.13 System Heat Gain 978
21.14 Cooling Load Estimate 982
21.15 Heating Load Estimate 983
References 991
Review Questions 992
22 Room Airflow and Duct Design 993–1050
22.1 Introduction 993
22.2 Continuity Equation 996
22.3 Momentum Conservation 997
22.4 Energy Equation 999
22.5 Static, Dynamic and Total Pressure 999
22.6 Pressure Drop 1001
22.7 Conversion from Circular to Rectangular Dimensions 1006
22.8 Minor Losses 1010
22.9 Airflow through Duct Systems with Fan 1020
22.10 Air Duct Design 1022
22.11 Room Air Distribution 1032
22.12 Air Distribution System Design 1043
References 1049
Review Questions 1050
23. Fans 1051–1070
23.1 Introduction 1051
23.2 Performance of Fans 1052
23.3 Fan Characteristics 1055
23.4 Vaneaxial Fan 1057
23.5 Fan Laws 1057
23.6 Fan Selection 1058
23.7 System Characteristics 1061
23.8 Ductwork in Series and Parallel 1062
23.9 Effect of Change in Fan Speed 1063
23.10 Effect of Change in Air Density 1064
23.11 Fan Installation 1066
23.12 Fans for Variable Volume Systems 1067
23.13 Fans in Series and Parallel 1068
Reference 1070
Review Questions 1070
Appendix 1071–1079
Index 1080–1087
1081
Index
Absolute zero, 38
Absorption refrigeration system, 351
ammonia absorption system, 352
comparison with mechanical vapour
compression system, 408
COP, 353
drawbacks of, 379
dual-effect system, 397
h–x diagram, 373
Platen–Munters system, 404
properties of refrigerant pairs, 407
water–lithium bromide system, 393
Adiabatic dehumidification, 766
Adiabatic demagnetization, 92
Adiabatic discharge temperature, 143
Adiabatic equivalent temperature, 832
Adiabatic mixing, 369
with heat rejection, 370
Adiabatic saturation temperature, 711, 753, 831
Adjusted dry-bulb temperature, 843
Air cleaning, 858
Air conditioning, 8
classification, 692–695
historical review, 689
a typical system, 994
Air distribution performance index (ADPI), 1044
Air liquefaction cycles, 648
Claude cycle, 654
Linde cycle, 651
Air–vapour mixture, 701
Air washer, 752
processes, 754
Aircraft refrigeration cycles
bootstrap system, 616
classification of, 610
comparison of, 624
cooling loads, 609
based upon DART, 625
reduced ambient, 622
with regeneration, 620
simple aircraft refrigeration system, 610
Amagat–Leduc’s law, 697
Apparatus dew point, 787, 792
Approach factor, 757
Aqua–ammonia solution
ammonia enrichment process, 380
cooling of, 372
enthalpy, 363
eutectic points, 361
heating of, 371
throttling, 373
vapour concentration, 363
vapour pressure, 361
Auto-cascade system, 347
Automatic expansion valve, 486
Availability, 33
Azeotropes, 453
maximum boiling, 453
minimum boiling, 453
1082 Index
Balancing the flow, 1027
Bell–Coleman cycle, 112
Bernoulli’s equation, 78, 999
Blackbody, 54
absorptivity, 56
emissivity, 56
monochromatic emissivity, 56
Boiling heat transfer, 67
Bubble point curve, 358, 438
Building related illnesses, 996
Bypass factor, 787
effect of, 800
typical factors, 789, 790
Capillary tube, 473
advantages/disadvantages of, 486
analysis of flow, 478
balance point between the compressor and the
capillary tube, 473
selection of, 478
Carnot heat engine, 33, 34
Carnot vapour cycle, 101
Cascade condenser, 320
Cascade refrigeration system, 320
applications of, 337
optimum intermediate temperature, 322
performance improvement of, 330
Ceiling diffuser, 1038
Chill factor, 995
Clapeyron equation, 48
Clausis inequality, 105
Closed system, 21
Clothing efficiency, 828
Clothing, evaporative resistance, 830
Clothing insulation, 827
Clothing, surface area, 830
Clothing, thermal and moisture resistance, 827
Coefficient of performance (COP), 99, 143
effect of refrigerant properties, 141
single stage saturation cycle, 141
suction state for optimum COP, 143
Comfort zone, 995
Complete vapour compression system, 571
performance of, 579
Compressors
aspirated volume, 180
centrifugal, 214
performance characteristics, 230
polytropic efficiency, 216, 217
pressure rise, 219
small-stage efficiency, 216, 217
work done, 219
clearance volume, 178
clearance volumetric efficiency, 180, 181
effect of pressure drops, 183
effect of heat transfer, 184, 185
hermetic, 197
overall volumetric efficiency, 186
power requirement, 187
actual compressor, 191
ideal cycle, 190
real
blowby, 194
effect of heat transfer, 194
effect of kinetic energy, 194
effect of leakages, 196
effect of speed, 196
effect of superheat, 195
reciprocating, 177
adiabatic discharge temperature, 249
choice of intermediate pressure, 254
coefficient of performance, 250
methods of improving, 250
mass flow rate, 245
optimum intermediate pressure, 258
pressure–volume diagram, 244
refrigeration capacity, 247
specific refrigeration effect, 247
swept flow rate, 248
volumetric efficiency, 245
work requirement, 246
rotary, 205
multiple van, 208
rolling piston, 205
rotating vane, 207
screw, 208
selection of, 239
superheating effect, 186
thermodynamics of, 172
Condenser, 505
circular plate fin, 517
fin efficiency, 514
heat transfer areas, 520
heat transfer coefficients, 523
performance characteristics, 573
rectangular continuous plate fin, 578
rectangular fin, 515
types of, 506
Condensing unit, characteristics of, 577
Condition line, 783
Convection, 59
Index 1083
Cooling load, 732
Cooling processes, 85
Daily range, 937
Dalton’s law, 699
Declination angle, 876, 877
Dehumidified air quantity, 792
Dehumidified temperature rise, 792
Dense air cycle, 605
Density, 23
Dew point curve, 358, 438
Dew point temperature, 43, 710
Diathermanous materials, 915
Diffusion
coefficient, 53
Fick’s law, 53
Direct expansion coil, 556
Displacement ventilation, 858
Domestic refrigerator, 7
Draft, 995
Draft coefficient, 963
Dry air, 42, 702
enthalpy of, 704
Dry Air Rated Temperature (DART), 625
Dry type evaporator, 553
Dubois area, 820, 824
Duct design, 1022, 1027
methods, 1025
equal pressure drop, 1029
static regain, 1030
velocity reduction, 1028
Ducts
air flow with fan, 1020
classification, 1024
effect of grille, 1012
loss in branches, 1019
loss in gradual expansion, 1014
loss in sudden contraction, 1015
loss in sudden expansion, 1012
losses at discharge, 1011
losses at inlet, 1010
material and construction, 1024
Ductwork
parallel connection, 1062
series connection, 1062
Dynamic loss coefficient, 1013
Effective Room Latent Heat (ERLH), 801
Effective Room Sensible Heat (ERSH), 801
Effective temperature, 832, 836, 843
Electronic type expansion valve, 501
Energy balance of human body
models, 824
Enthalpy, 31, 39
of moist air, 711
potential, 560
of evaporation, 4
Entropy, 32, 33, 35, 36, 38
Environmental indices, 836
Equation of state, 38, 40
Beattie Bridgman equation, 41
Benedict–Webb–Rubin (BWR)
equation, 41
Canahan–Starling–Desaints, 445
Cubic equation of state, 443
Dieterici equation, 41
Martin–Hu (MH) equation, 42, 445
Peng–Robinson equation, 41, 444
Redlich–Kwong equation, 41, 444
Soave Redlich–Kwong equation, 444
Van der Wall’s equation, 40, 444
Virial equation of state, 443
Equation of time, 877
Equilibrium construction lines, 366
Equivalent temperature difference, 947
Evaporative coding, 2
Evaporator(s), 4
bonded plate, 557
classification of, 549
finned, 558
flooded, 551
performance characteristics, 576
shell-and-tybe type, 552, 553
starving of, 581
Ewing’s construction, 143, 145
Excess property, 440
Expansion valve, 473
characteristics, 577
some practical problems, 502
types of, 473
Fans
axial, 1052
centrifugal, 1052, 1053
characteristics, 1055, 1061
installation, 1066
laws, 1057
performance of, 1052, 1063
selection, 1058
speed, 1063
system effect factor, 1066
vaneaxial, 1052
Flash chamber, 284
1084 Index
Flash intercooler, 272
Float type expansion valve, 499
Floor registers, 1038
Flow work, 30, 79
Fluid flow, 77
Force, 22
Free jet, 1033
entrained air, 1034, 1035
induction ratio, 1035
primary air, 1034, 1035
surface effect, 1035, 1036
total air, 1035
Freezing point, 43
Friction factor, 83, 1002
Frictional pressure drop, 1001
Gas cycle refrigeration
actual cycle, 592
Bell–Coleman, 588
effect of pressure ratio on performance, 589
Joule cycle, 588
effect of pressure drops, 598
variation of COP with pressure ratio, 591
open at the warm end, 606
Regenerative Joule cycle, 601
Reversed Brayton cycle, 588
Reversed Cornot cycle, 586
Gibbs–Dalton’s law, 699
Gibbs function, 36
Glide temperature, 439
Global warming, 421
Global Warming Potential (GWP), 432
Grand total heat (GTH) load, 795
Gray body, 56
Gregorian correction, 873
Heat exchanger, 75
Heat transfer, 25, 27, 50
coefficients, 71, 834
combined convection and radiation, 70
condensation, 66
conduction, 50
Fourier’s law, 51
conduction equation, 52
correlations, 63
evaporative, 825
periodic through a wall, 936, 940
radiation, 58
through walls and roofs, 936
Heating load, 732
Heating Ventilating and Air Conditioning (HVAC)
system, 691, 993
elements of, 994
Helmholtz function, 36
Homogeneous mixture, 697
Humid air specific heat, 711, 733
Humid operative temperature, 832, 836
Humidification process, 734, 735
Humidity measurement, 781
dew point indicator, 782
Humidity ratio, 707, 781
Hydrocarbons, 413
Hydrodynamic boundary layer, 60
Hygrometer, 781, 782
Hygroscopic spray, 757
Ideal solutions, 354
Index run, 1027
Indoor air quality (IAQ), 731, 847
methods, 851
Infilteration, 956
methods for estimating, 956
Internal energy, 29, 39
Inversion curve, 89
Isentropic efficiency
of compressor, 125
Isomers, 412
Joule cycle, 112
analysis for perfect gas, 114
Joule–Thomson coefficient, 88, 89, 584
Kelvin–Planck statement, 100
Kinetic energy, 27
Kirchhoff’s law, 56
Kyoto Protocol, 433
Latent heat, 4, 732
Liquid chillers
double pipe, 555
shell-and-coil, 554
Log mean temperature difference
for crossflow heat exchanger, 510
for water-cooled condenser, 532
Mass fraction, 354
Mass velocity, 479
Index 1085
Maxwell’s relations, 37
Mean radiant temperature, 842
Melting point, 43
Metabolic rate, 820, 822
basal, 821
heat generation values, 821
Minor losses, 1001, 1010
in bends, elbows and tees, 1016
Mixture of ideal gases
Dalton’s law of partial pressures, 40
Mixtures
cubic equations, 449
cycle diagrams, 451
equations of state, 448
Helmholtz energy, 450
non-azeotropic, 413
ozeotropic, 413
Modified effective temperature, 839
Moist air, 39
adiabatic mixing of two streams, 740
with condensation, 742
Mole fraction, 355
Montreal Protocol, 433
Multistage systems, 270
intermediate pressure, 280
limitation of, 318
multi-evaporator, 303
one compressor and two evaporators, 303
two compressors and two evaporators, 309
oil wondering, 280, 319
temperature ranges, 291
Natural convection coils, 550
Natural ice, 2
Navier Stokes equations, 998
Nocturnal cooling, 2
Noise, 1042
Nonideal solutions, 356
Normal boiling point, 43
Occupied zone bypass factor, 853
Open system, 21
Operative temperature, 825, 843
Outside air latent heat (OALH), 795
Outside air sensible heat (OASH), 795
Outside air total heat (OATH), 795
Ozone Depletion Potential (ODP), 432
Particulate matter, removal of, 859
Perfect gas, 38
Perpetual Motion Machine of First Kind (PMMFK),
32
Physiological hazards, 834
Planck’s law, 54
Point function, 29
Pollutants, 848
Potential energy, 27
Power, 28
Predicted Mean Vote (PMV), 839
Predicted Percentage of Dissatisfied (PPD), 839
Pressure, 23
Processes
irreversible, 32, 33, 35
reversible, 32, 33
Pulse tube, 637
Pure humdification, 736
Pure substances, 43, 358
Psychrometer
practical use of, 772
theory of, 765
Psychrometric parameters, 836
Psychrometric processes, 732
Ram effect, 611
Ram efficiency, 612
Raoult’s law, 355
Recovery
factor, 586
temperature, 586
Refrigerant tables, 130
Refrigerants, 9
alternatives, 432, 456
classification of, 410, 411
commonly used, 414
designation of, 411
desirable properties of, 415
GWP of, 433
high normal boiling point, 428
low normal boiling point, 428
mixtures of, 436
temperature–composition diagram, 438
natural, 462
ODP of, 433
reaction with lubricating oils, 423
reaction with moisture, 425
thermodynamic properties, 426
types of, 411
Refrigerating efficiency, 125
Refrigeration, 98
gas cycle, 13
magnetic, 16
1086 Index
mechanical vapour compression, 3, 5
solar energy based, 12
steam jet, 14
thermoelectric, 15
vapour absorption, 11, 12
Refrigeration capacity, 28, 99
Reflectivity, 57
Regain, 998
Relative humidity, 709
Respiratory losses, 826
Reversed Brayton cycle, 112
Reversed Carnot cycle, 100, 108, 126
with saturated vapour, 118, 119
with wet vapour, 116, 117
Reversed Cornot theorems, 104
Reversible heat engine, 100
Reversible refrigeration system, 103
Reynolds analogy
Room air
drop, 1032
distribution patterns, 1037
entrained, 1033
motion, 1036
throw, 1032
Room Latent Heat (RLS) load, 790
Room Sensible Heat Factor (RSHF) line, 792
Room Sensible Heat (RSH) load, 790
Room total heat (RTH) load, 791
Saturated
air, 701, 707
liquid, 43
liquid line, 44
vapour, 43
vapour line, 44
Saturation, degree of, 709
Saturation pressure, 4
Saturation properties, 47
Saturation temperature, 43
Sensible cooling, 732
Sensible heat factor, 739
Sensible heat transfer, 824
Sensible heating, 732
Sensible loads, 732
Sick building syndrome, 996
Simple summer air conditioning system, 791
with ventilation and non-zero bypass factor,
799
with ventilation and zero bypass factor, 794
Single stage saturation (SSS) cycle, 121, 126
performance of, 137
Solar angles
basic, 875
derived, 878
Solar constant, 888
Solar heat gain factor (SHGF), 820
Solar radiation intensity
direct beam radiation, 889
on earth’s surface, 890
reflected radiation, 889
sky radiation, 889
Solution
properties of, 354
temperature–composition diagram, 357,
359
Specific heat
at constant pressure, 25
at constant volume, 25
Specific refrigeration effect, 142
Specific volume, 23
Specific work, 143
Spray washer, 753
Sprayed coils, 758
Stack effect, 963
Stagnation
enthalpy, 586, 611
temperature, 586
Standard effective temperature, 837, 843
Standard vapour compression cycle, 121, 122
Static regain, 82, 1001, 1013
Static temperature, 586
Steam-jet ejector system, 664
advantages and limitations, 669
performance, 670
Stefan–Boltzmann law, 55
Stirling cycle, 641
actual cycle, 648
analysis of, 643
refrigeration effect, 645
Stratification factor, 854
Subcooling, 132
Sublimation process, 44
Superheating, 135
Temperature, 24
Thermal boundary layer, 60
Thermal comfort, 820, 823, 839
Thermal conductivity, 51
Thermal diffusivity, 52
Thermal environment, 839, 872
Thermal radiation, 54
Thermal sensation, 839, 840
Index 1087
Thermodynamic
equilibrium, 20
property, 20
state, 20, 21
Thermodynamics,
first law, 29
for a closed system, 30
four laws of, 28
fundamental relations, 36
for an open system, 31
second law, 32
Clausius inequality, 35
Clausius statement, 32
Kelvin–Planck statement, 32
third law, 38
zeroth law, 28
Thermoelectric cooling, 91, 674
Thermoelectric refrigeration, 677
Thermoregulatory mechanisms, 832, 833, 834
Thermostatic expansion valve, 492
Total latent heat (TLH), 795
Total sensible heat (TSH), 795
Transmissivity, 57
Triple point, 43
Throttling, 88, 584
Trouton number, 49, 427
Turbulent flow, 60
Vapour compression cycle, 98, 121
actual cycle, 148, 150
heat transfer, 148
isentropic efficiency, 148
pressure drops, 148
with subcooling, 133
with superheating, 135
ten point cycle, 153
Vapour pressure, 4
Velocity pressure, 958, 999
Ventilation efficiency, 854
Virial equation of state, 42, 702
Volumic refrigeration capacity, 124
Volumic refrigeration effect, 139, 142
Vortex tube, 16, 93, 633
advantages and disadvantages, 637
analysis of, 636
counterflow type, 634
uniflow type, 635
Wake, 958
Water refrigeration, 659
centrifugal compressor-based 661
principle of evaporation, 660
Water vapour
enthalpy of, 704
properties of, 703
Wet-bulb temperature, 711, 712
psycholometer, 773
thermodynamic, 773
Wet finned-tube heat exchanger, 564
Wetted fin
efficiency of, 561
overall heat transfer coefficient, 562
Wetted surface, 761
Wien’s displacement law, 55
Z-transform methods
conduction transfer functions, 955
response factors, 955
كلمة سر فك الضغط : books-world.net
The Unzip Password : books-world.net
أتمنى أن تستفيدوا من محتوى الموضوع وأن ينال إعجابكم
رابط من موقع عالم الكتب لتنزيل كتاب Refrigeration and Air Conditioning
رابط مباشر لتنزيل كتاب Refrigeration and Air Conditioning 
|
|







